Hyperscalers: The Complete Guide to What, Why and How
Orinal source post by Melissa Palmer
We’ve heard a lot about hyperscalers over the last several years as public cloud adoption began to rise. Now, they’ve become a central part of global IT infrastructure and essential to operations. There are many reasons to choose a hyperscaler as your cloud provider, so let’s take a closer look at what a hyperscaler is and how it can be leveraged for your organization.
What is a Hyperscaler?
A hyperscaler is a type of large-scale data center that offers massive computing resources, typically in the form of an elastic cloud platform. Organizations use them to deploy and manage large-scale applications and services.
There are many similarities between a hyperscaler and the on-premises data centers many of us are used to operating. As the name implies, the big difference is the scale at which they operate, which fundamentally changes how things are designed and architected.
For example, in a small data center I once worked in, we had six-node hypervisor clusters and had to plan for things like the failure of a node. In this small environment, it was important to fix a failed node as quickly as possible because we didn’t have the capacity to run with two failed nodes.
If these clusters were in a hyperscale datacenter like AWS, we wouldn’t have worried about a two-node failure. Things would be designed and architected in a way that clusters could survive even if many nodes failed. If they ran out of capacity, the services running on them could easily be re-directed.
Chances are you’ve already worked with a hyperscaler, and it’s likely to be one or more of the industry leaders.
Who Are the Top 5 Hyperscalers?
The “big dogs” in the field are Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), IBM cloud, and Oracle, which all offer large-scale solutions. Not only do they offer services to their customers, but they run their own applications within their hyperscaler cloud.
You may have heard these referred to as simply cloud service providers, or the public cloud. They are all of these things, but operate at a much larger scale than most other providers.
Facebook is also considered a hyperscaler, but they’re a bit unique since they don’t offer their services to any customers—they use them to run their own applications.
Why Do Companies Leverage Hyperscalers?
There are a few reasons that companies might use hyperscalers. One reason is that they offer massive scale, performance, and reliability. Companies also don’t need to worry about their infrastructure or where it runs—no more worrying about data center space, power, cooling, or how long the lead time may be if you need to order more servers. There’s no worrying about standardizing on a particular hardware ecosystem since you no longer need to worry about replacing or troubleshooting hardware.
Because hyperscalers offer such scale, they’re often also attractive for companies that need to deploy large-scale applications or services, especially if they need to scale these applications at specific time periods. Think things like month-end processing or a retailer scaling capacity during the holiday shopping season.
Hyperscalers often have a global footprint, which is important for multinationals. They can easily deploy applications in different locations to be sure to provide the best service to their local customers.
Hyperscalers are also great for big data and analytics. These types of applications sometimes require massive capacity only during data processing, so if they were deployed in a traditional data center, there would be a lot of wasted cycles while equipment sat idle. These wasted cycles would add up to a tremendous cost over time.
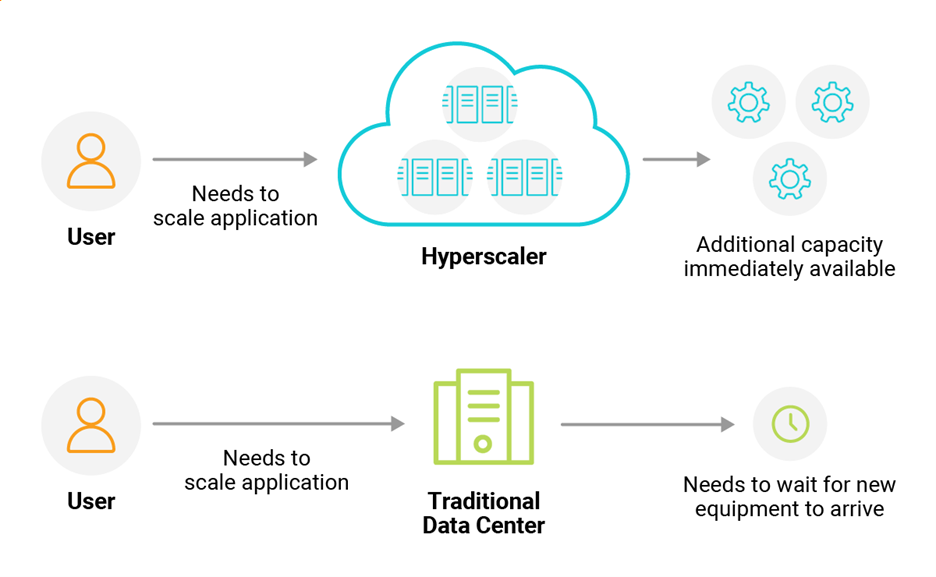
FIGURE 1 – SCALING AN APPLICATION
How Do Companies Decide What to Put in a Hyperscaler Cloud?
Choosing what workloads to operate in a hyperscaler does take some thought and planning since services aren’t free. Here are some best practices for guiding your adoption of hyperscalers.
Focus on the Applications
Focus on the applications that will benefit from scale. If your application requires more resources than your data center can provide, it may be a good candidate to move to a hyperscaler cloud. If you plan on massive growth or peak utilization, a hyperscaler can also be a good candidate.
Get Ready to Be Flexible
One significant benefit of hyperscale computing is its flexibility. It’s simple to deploy applications and services and begin using them. Be aware, however, of the special considerations necessary to ensure your application is designed to take advantage of the full feature set. This can come with a learning curve for both application development and operations teams.
Use APIs
Hyperscalers provide APIs for users to take full advantage of their platform. While there are always web portals and interfaces that can be used for management, APIs can be used to automate most common tasks, such as scaling systems up or down.
This was my biggest personal learning curve when it came to using services. If we use the example of AWS, new services are constantly being released, and finding them in the portal can be a bit overwhelming. With just a few lines of code, services can be used without digging around in a portal and wasting time.
Hyperscalers are unique platforms that offer massive scale, performance, and reliability. They’re often used for large-scale applications or services because of their global footprint and ability to deploy in different locations easily.
Companies should focus on what workloads will benefit from running in a hyperscaler cloud before deciding to move. If you’re leveraging hyperscaler data center and looking for an observability solution to help you streamline operations even further, be sure to check out the SolarWinds Platform.
The post Hyperscalers: The Complete Guide to What, Why and How appeared first on Orange Matter.